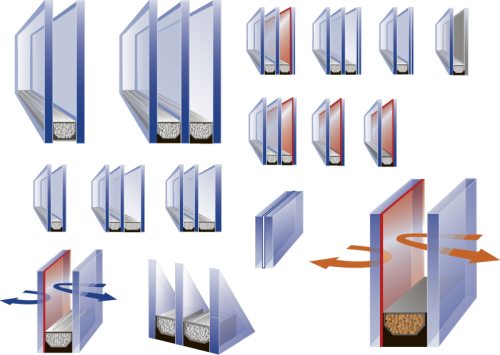
Insulation glazing is an element, in which two or more glazings have been attached airtightly together with molding on the rim and elastic masses.
Insulation glazing is used for example in window structures, front doors, glass deckings and facade glazing.
Insulation glazing is manufactured with the so-called two-phase method, in which the aluminum molding used in between the glazings is sealed in two phases. The purpose of the inner seal is to keep humidity outside the gap space and at the same time form a heat-insulating film between the glass and the metal molding.
The outer seal forms the actual elastic bond between the glass and the molding.
Grainy dehumidifier is placed inside the hollow molding to remove any possible humidity that has gotten into the gap in the manufacturing phase.
In addition to surface glazing, it is possible to use special glazing such as bullet resistant, burglary proof or fire resistant glazing in insulation glazing.
Energy saving glazing, i.e. selective glazing, is made from bright glazing that is coated with a selective coating. Energy saving glazing lets the Sun’s short-waved radiant energy through, while at the same time reflects back the long-waved heat radiation that is trying to exit the room.
The U-value of glazing tells how much energy as watts one square meter of glass lets through when the temperature difference is one degree celsius (W/m2K). That is to say, the U-value describes the glazing’s heat-technical performance. The smaller the U-value, the better the glazing’s heat-technical performance. Optical performance is described with for example light permeability LT and solar energy total permeability TST (g).
Insulation glazing is always tailor-built.
Gases
When manufacturing insulation glazing, also other gases besides air can be used in the gaps. They can help in improving the glazing’s heat insulation and soundproofing.
The gases diffuse slowly. The speed of diffusion is not constant and so difficult to verify. Temperatures, type of seal mass, and the gas affect the speed of diffusion.
Below are some of the most commonly used gases:
Argon (Ar) – is a gas that is condensed from the atmosphere. It improves heat insulation and is fairly inexpensive.
Krypton (Kr) - is a gas that is condensed from the atmosphere. It improves heat insulation somewhat more than argon, but is significantly rarer and more expensive noble gas.